Aquafaba
Legumes, which play a crucial role in the human diet since ancient times, are still appealing to a broad range of consumers due to their low-fat, high carbohydrate, and protein contents. In addition to consumption, it is a critical product group in terms of sustainability of agricultural production and environmental protection due to its contribution to let free nitrogen in the air to bind to the soil and to reduce fallow lands in agriculture. Among the legumes, which is a huge family, that includes different types of beans, lentils, chickpeas, peas, and soya; beans, lentils, and chickpeas are the most produced ones in Turkey and in all over the world. In fact, according to TÜİK statistics, in 2018, 51.5% of legume production belonged to chickpeas, 25.3% were red lentils, and 18.0% were dry beans.
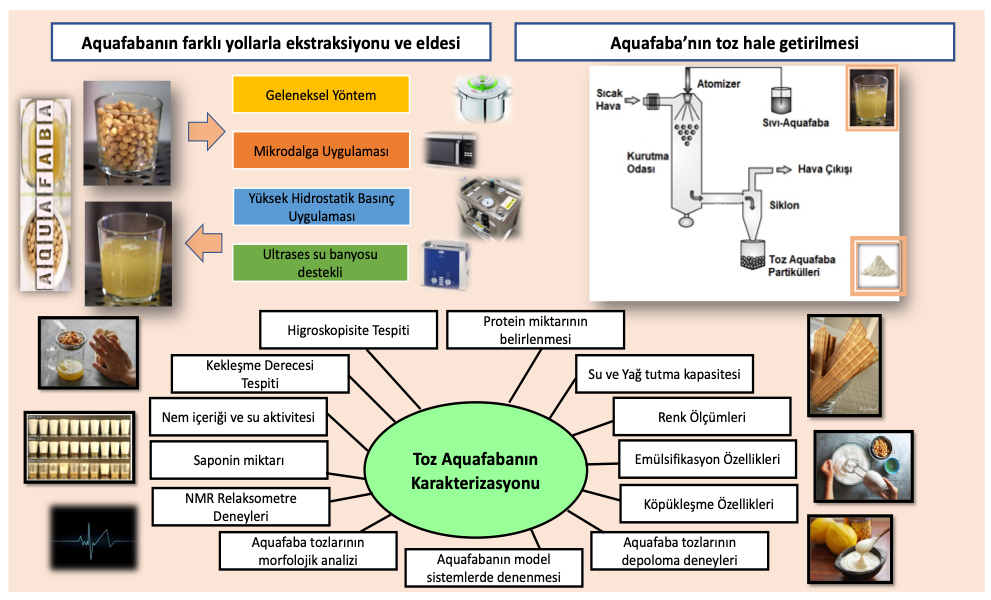
In this project, we will focus on the boiled water of the chickpeas which we can also consider as a waste of processing. Within the scope of the project, chickpea water, also known as aquafaba, will be obtained using different technologies; it will be pulverized, and a powder emulsifier will be produced. The aim of the project is one-to-one harmony with the section of innovative additives production in the priority areas of TUBITAK 2020. Aquafaba, with its functional properties similar to egg white, has become very popular as an alternative emulsifier and foaming agent. The biggest advantage of the aquafaba is that it is of vegetable origin. In this regard, the use of aquafaba in kitchens has become widespread, as the food options of consumers suffering from milk allergy, lactose intolerance or those who prefer a vegan/vegetarian diet have increased. It is known that, aquafaba does not contain starch and oil and as dry matter it consists of proteins and polysaccharides of which most are fibers. It also has some other compounds (saponin, etc.), which are known to enhance properties like emulsifying and foaming. Especially, the formation of a stable foam made the aquafaba very advantageous. Aquafaba is literally obtained through boiling chickpea in a pressure cooker or boiling it in a pan for long times. In this project, different food technologies will be tested in aquafaba production. Microwave, high hydrostatic pressure (HHP), ultrasound techniques have been proven in many studies to increase the extraction efficiency in foods. By using these three techniques, the dry matter amount of the aquafaba is expected to be increased. Moreover, physicochemical properties of the products will also be improved. The aquafaba obtained with these processes will then be pulverized in a spray dryer and a powder emulsifier will be obtained for the food industry.
Market researches showed that there exits an aquafaba powder produced by an American company through the traditional ways of production. The unique feature of this project is that different technologies will be utilized when producing aquafaba and the effect of these technologies on aquafaba powders will be investigated. A comprehensive physical characterization (moisture, water activity, color, hygroscopicity, caking, emulsification, foaming, amount of protein / saponin; morphological analysis) of the aquafaba powder obtained will be performed and the aquafaba will be tested on cakes, meringue and mayonnaise. Upon completion of the project, an emulsifier with plant origin that is not yet present in our country and which expected to have better properties than the ones in the international market will be obtained. Moreover, scientific publications, invention/patent applications; new reserach proposal offers and training young researchers will be just some of the outcomes of the project.